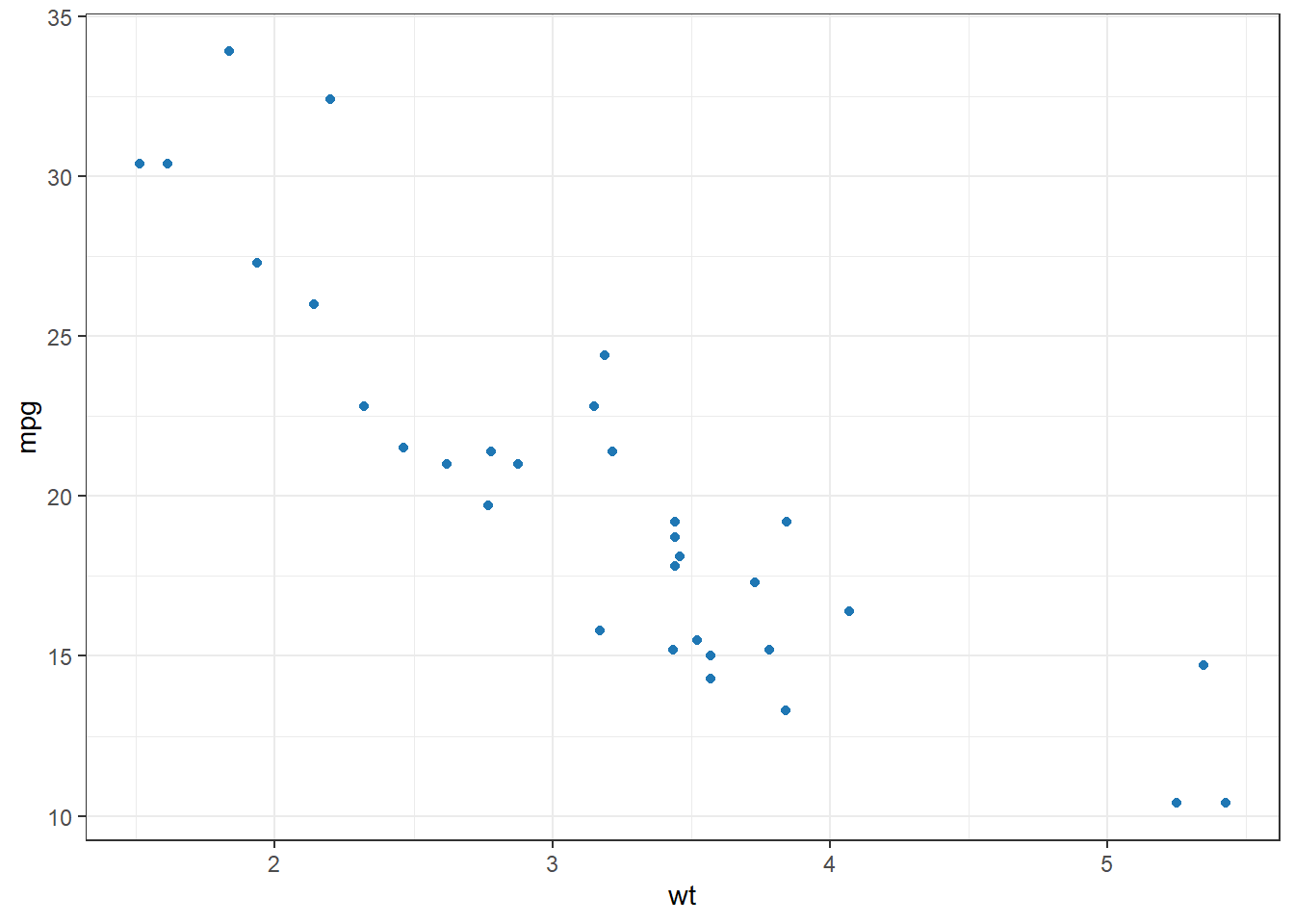
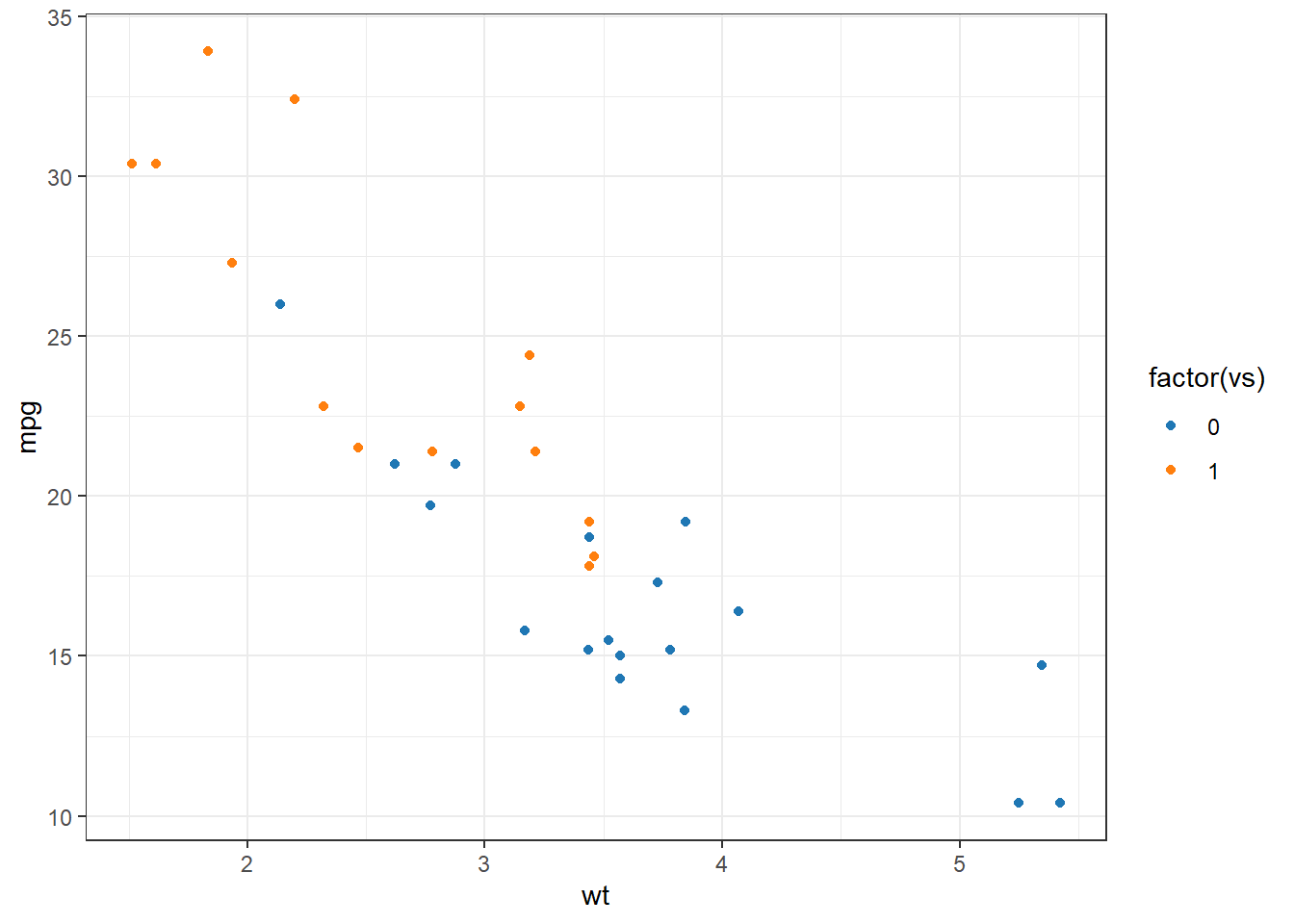
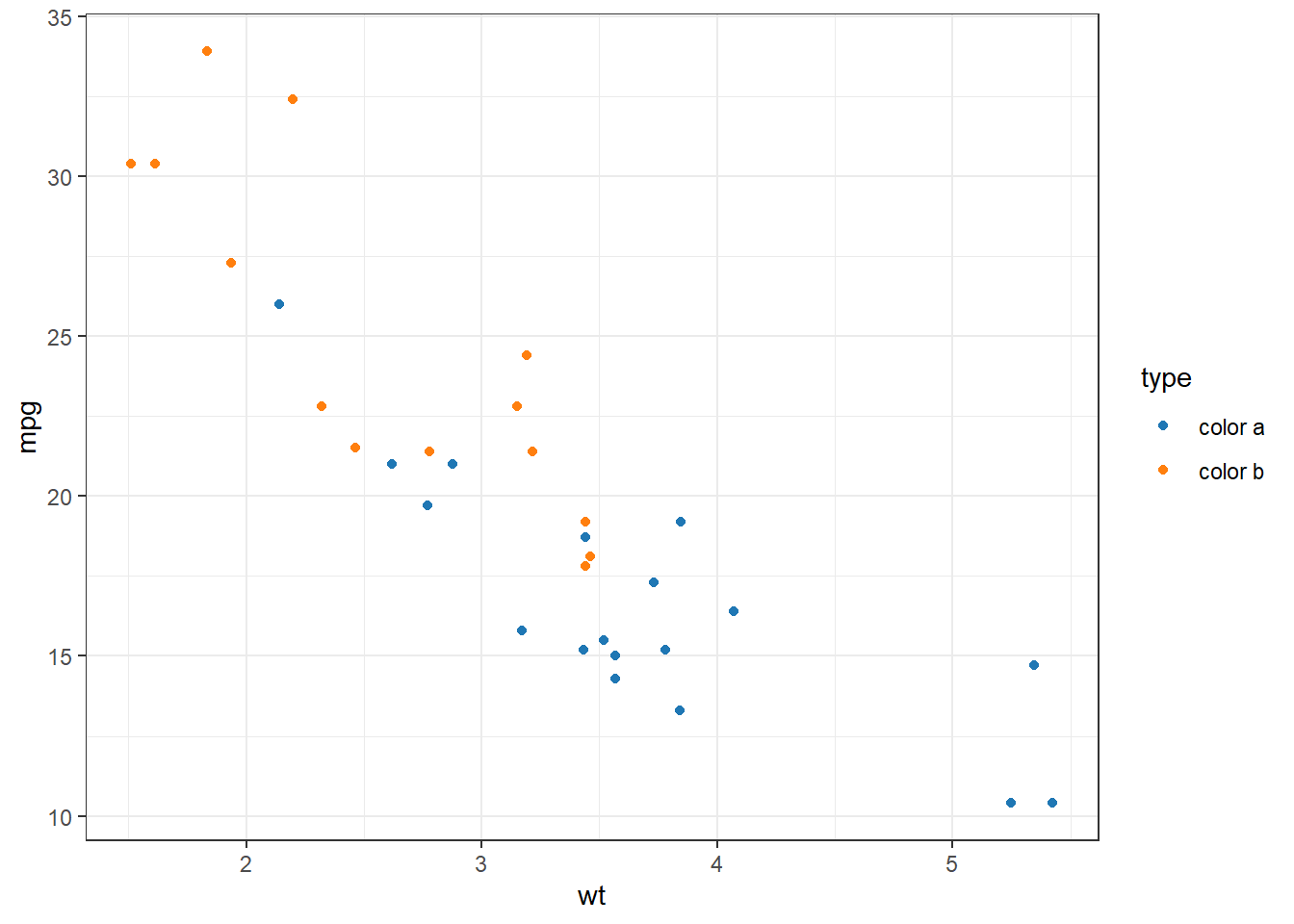
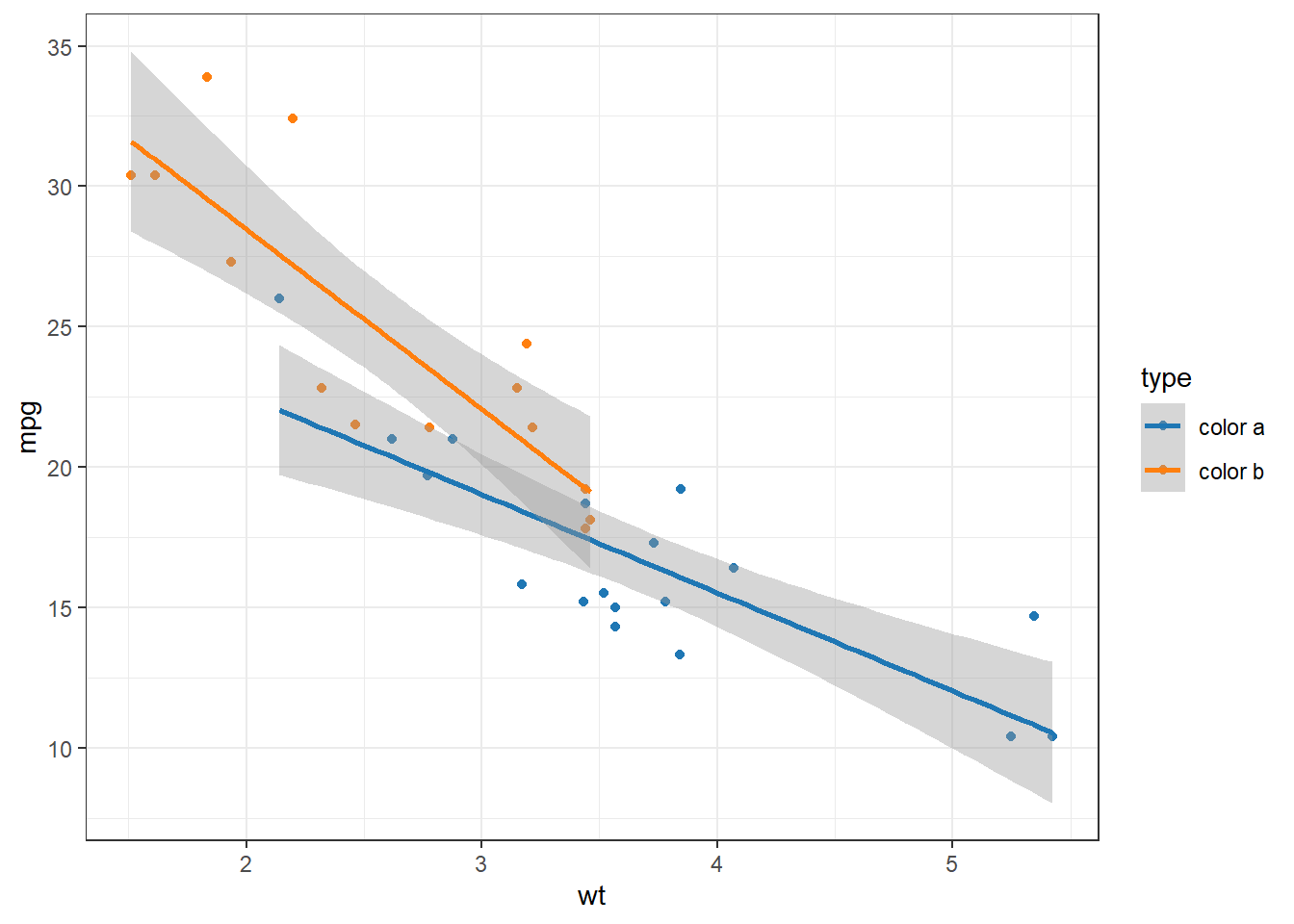
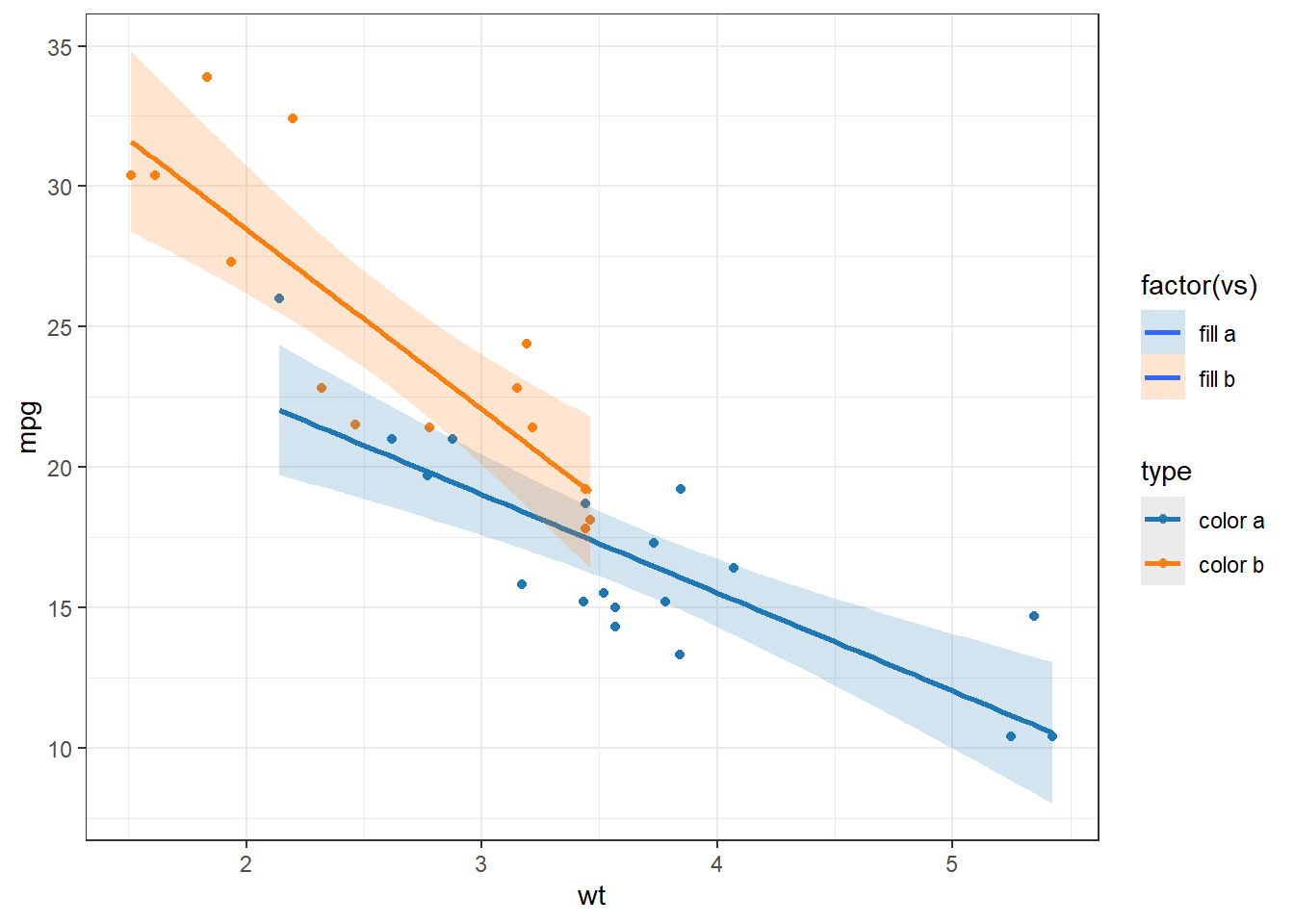
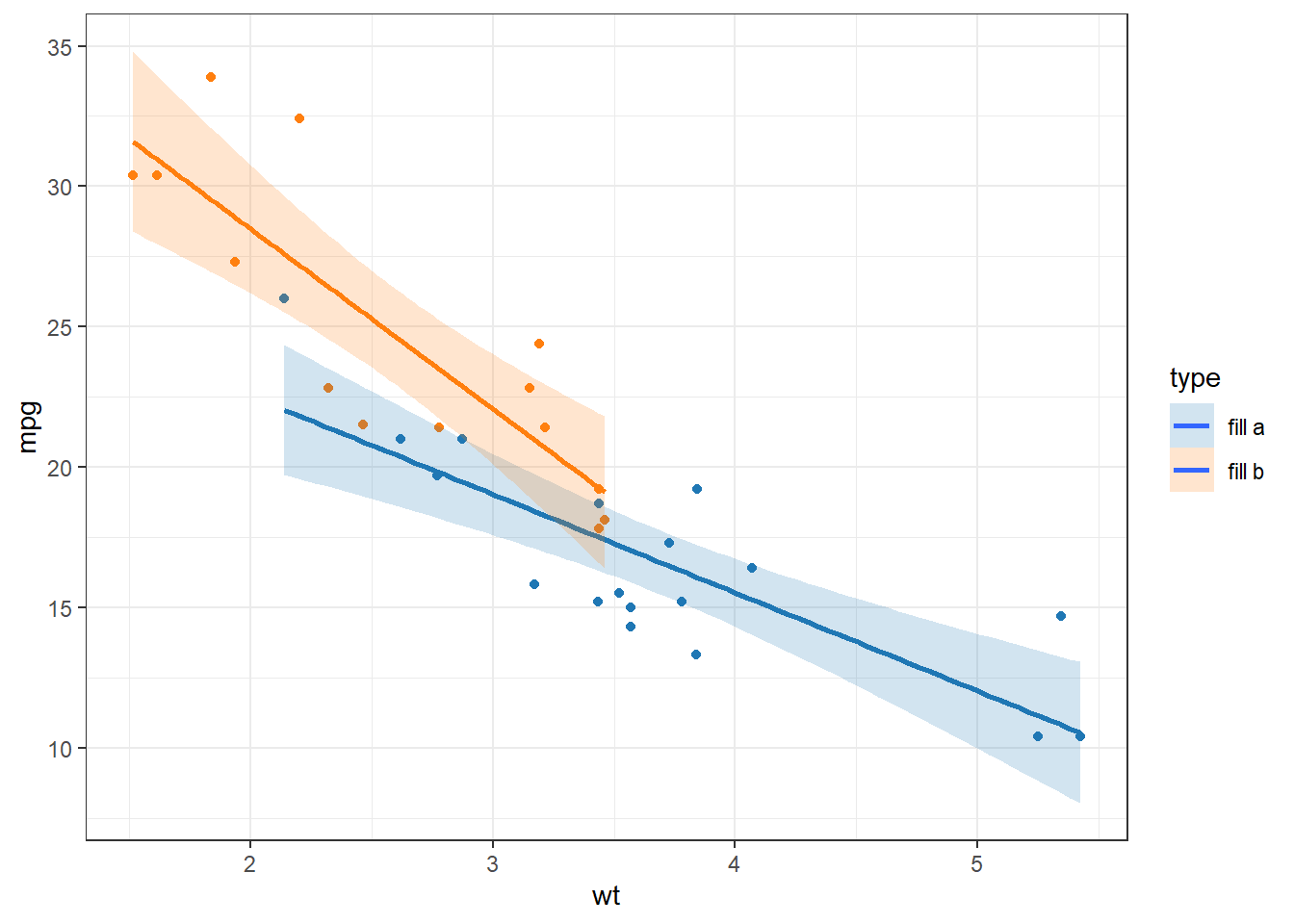
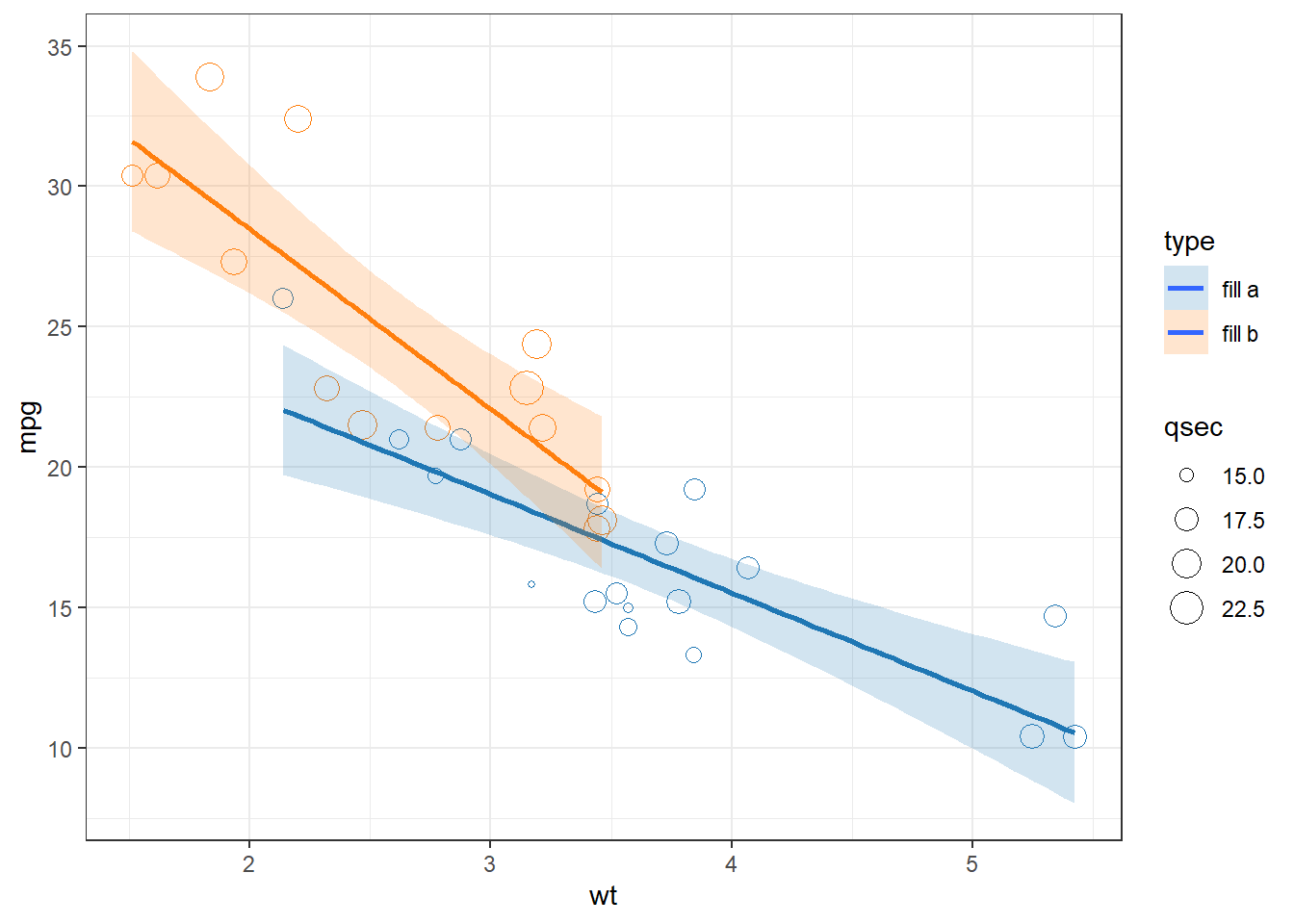
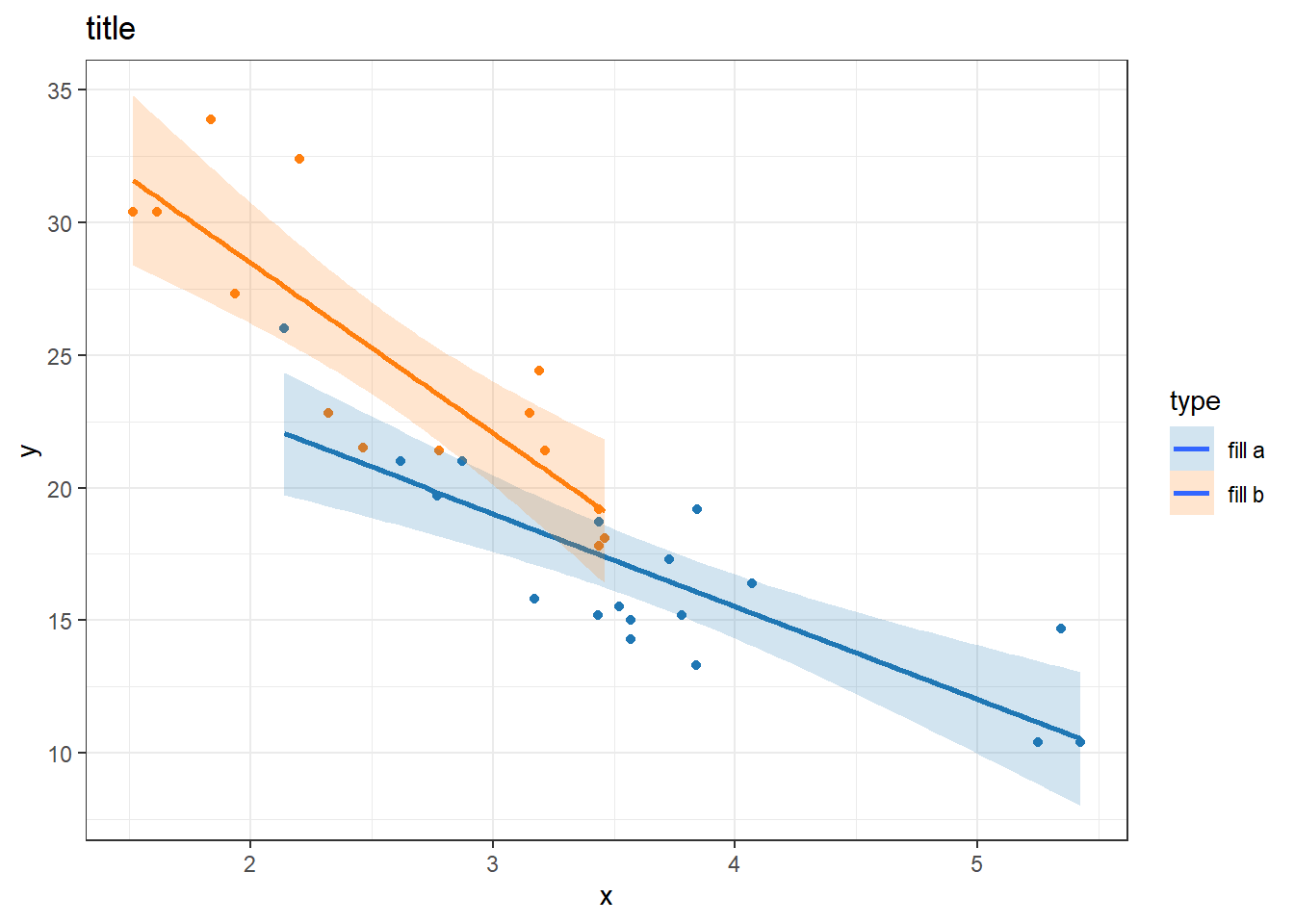
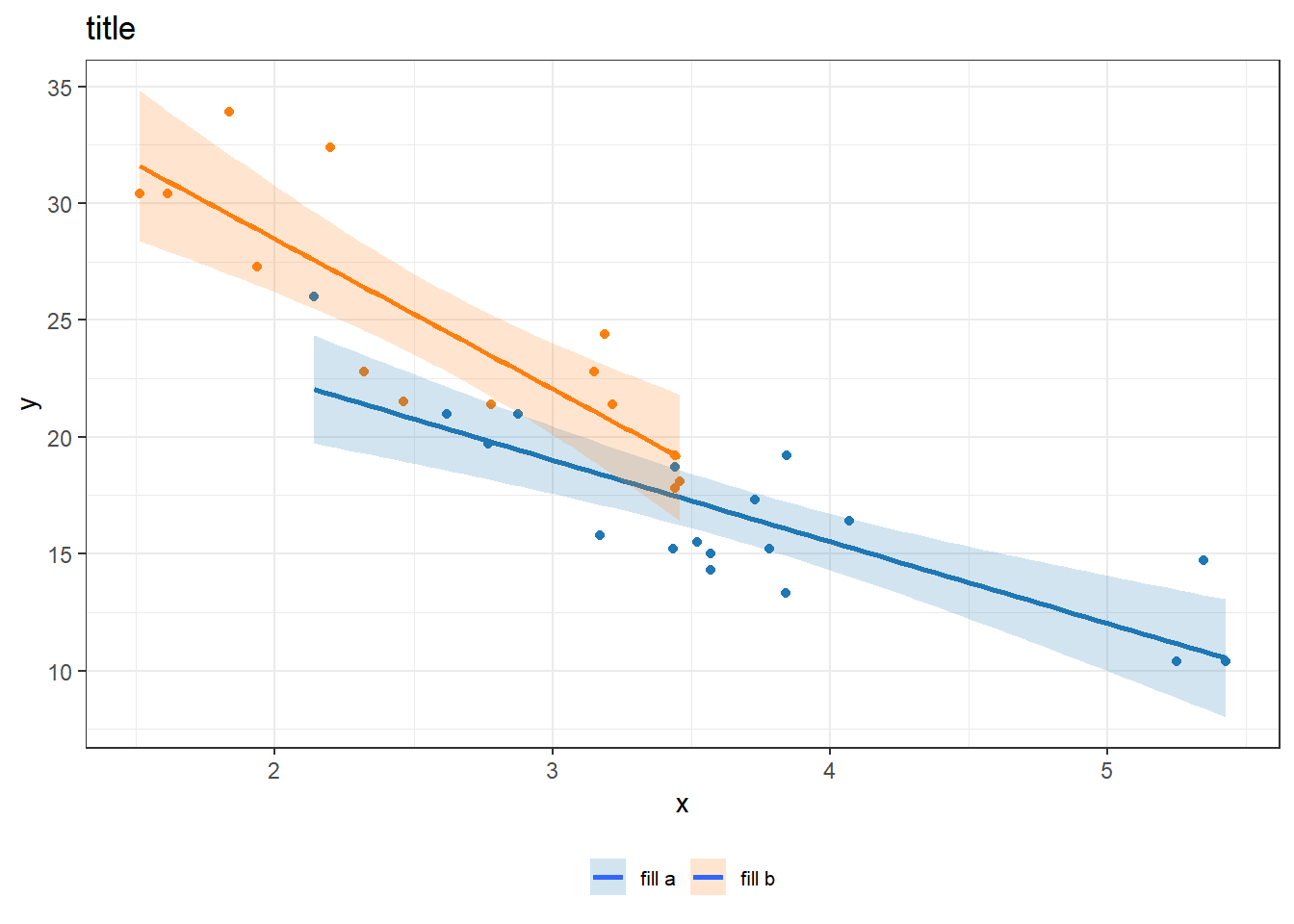
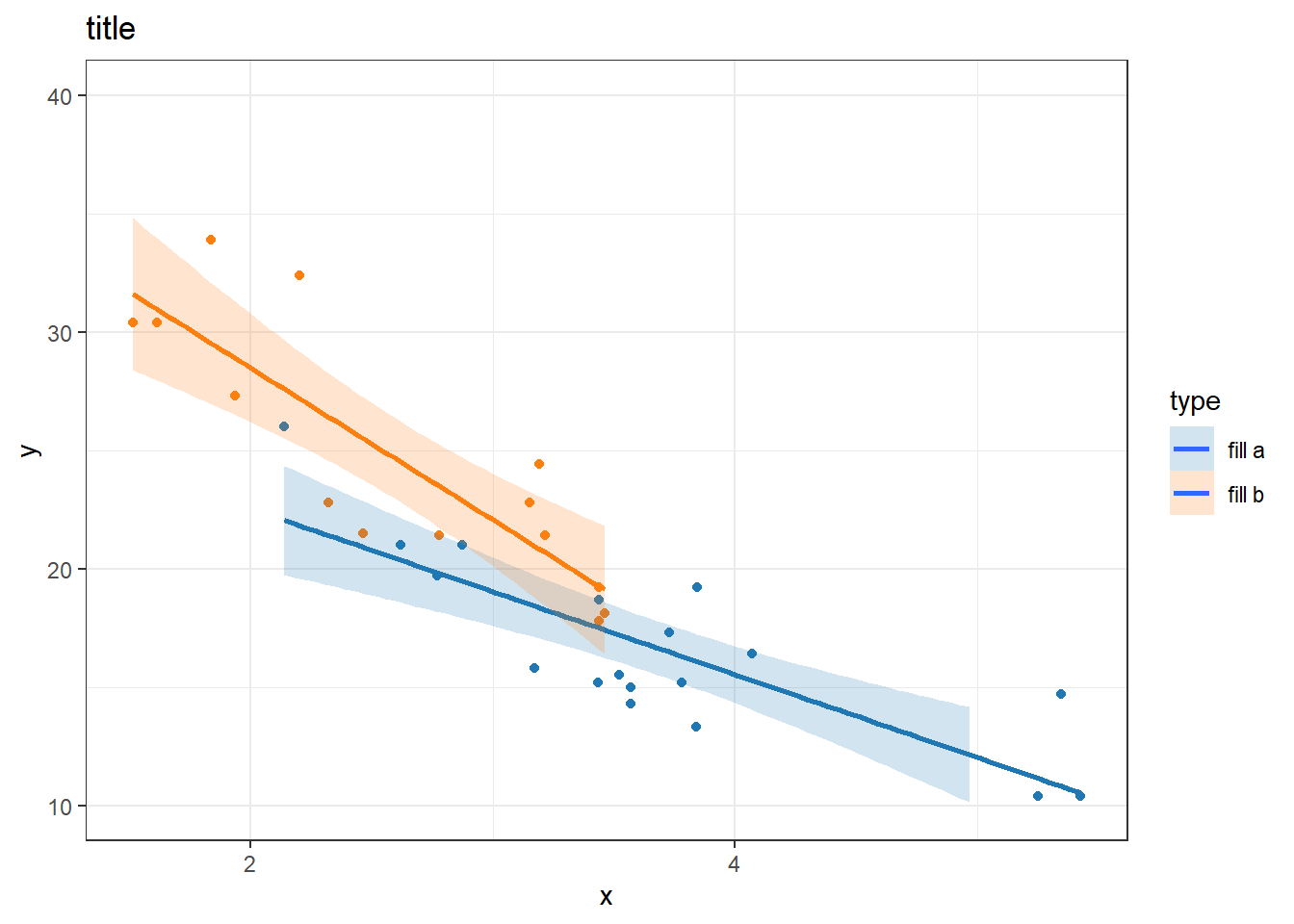
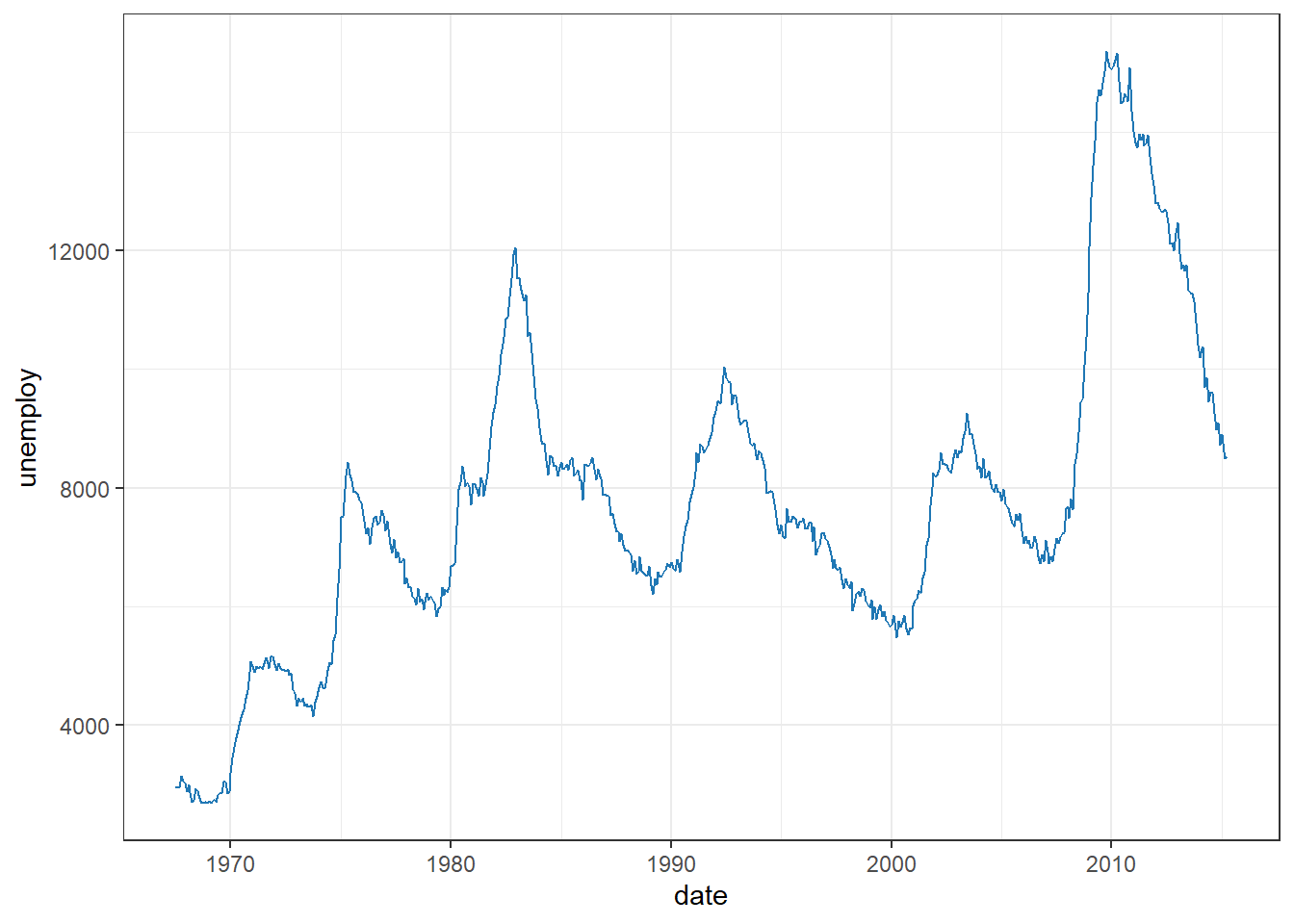
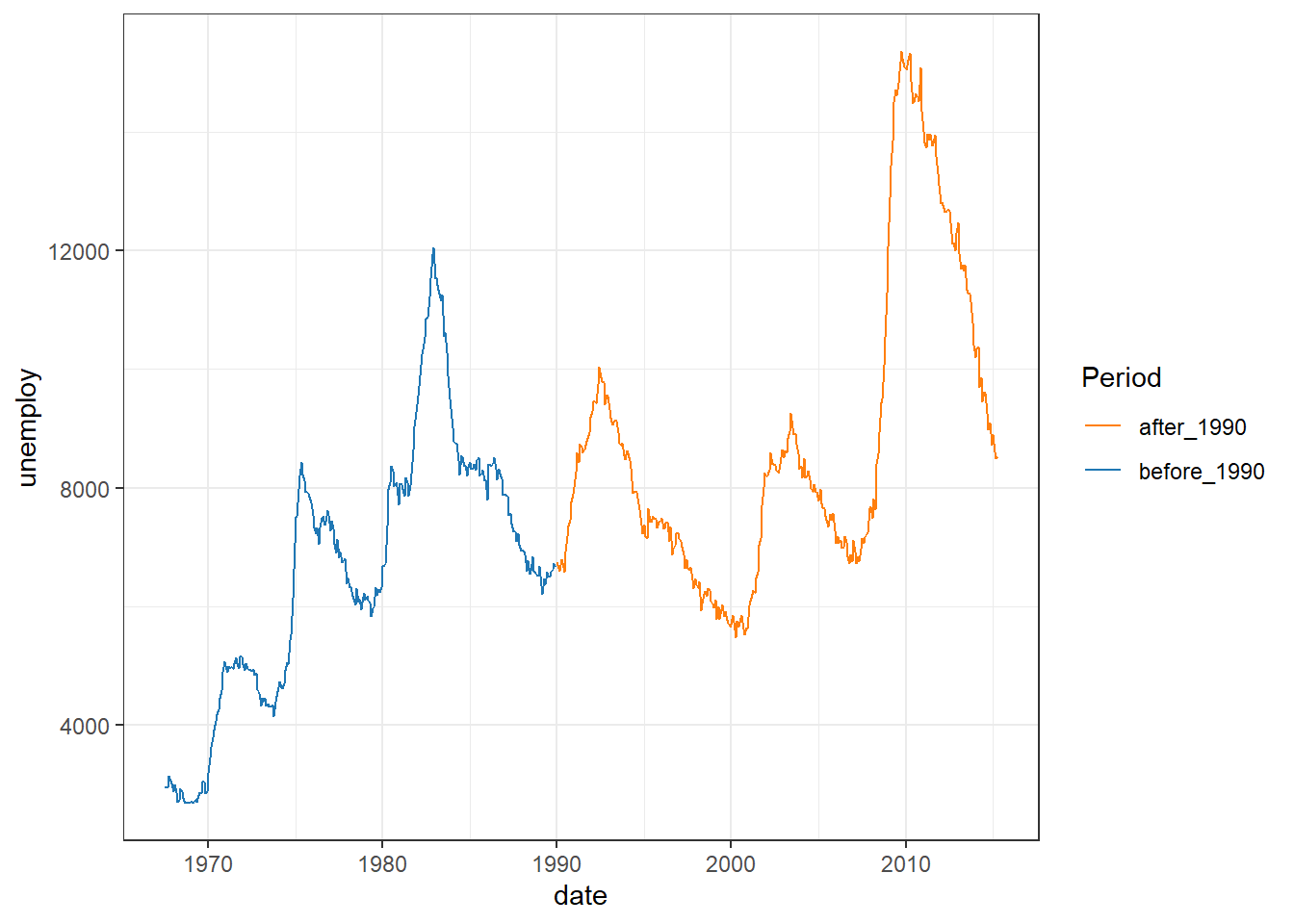
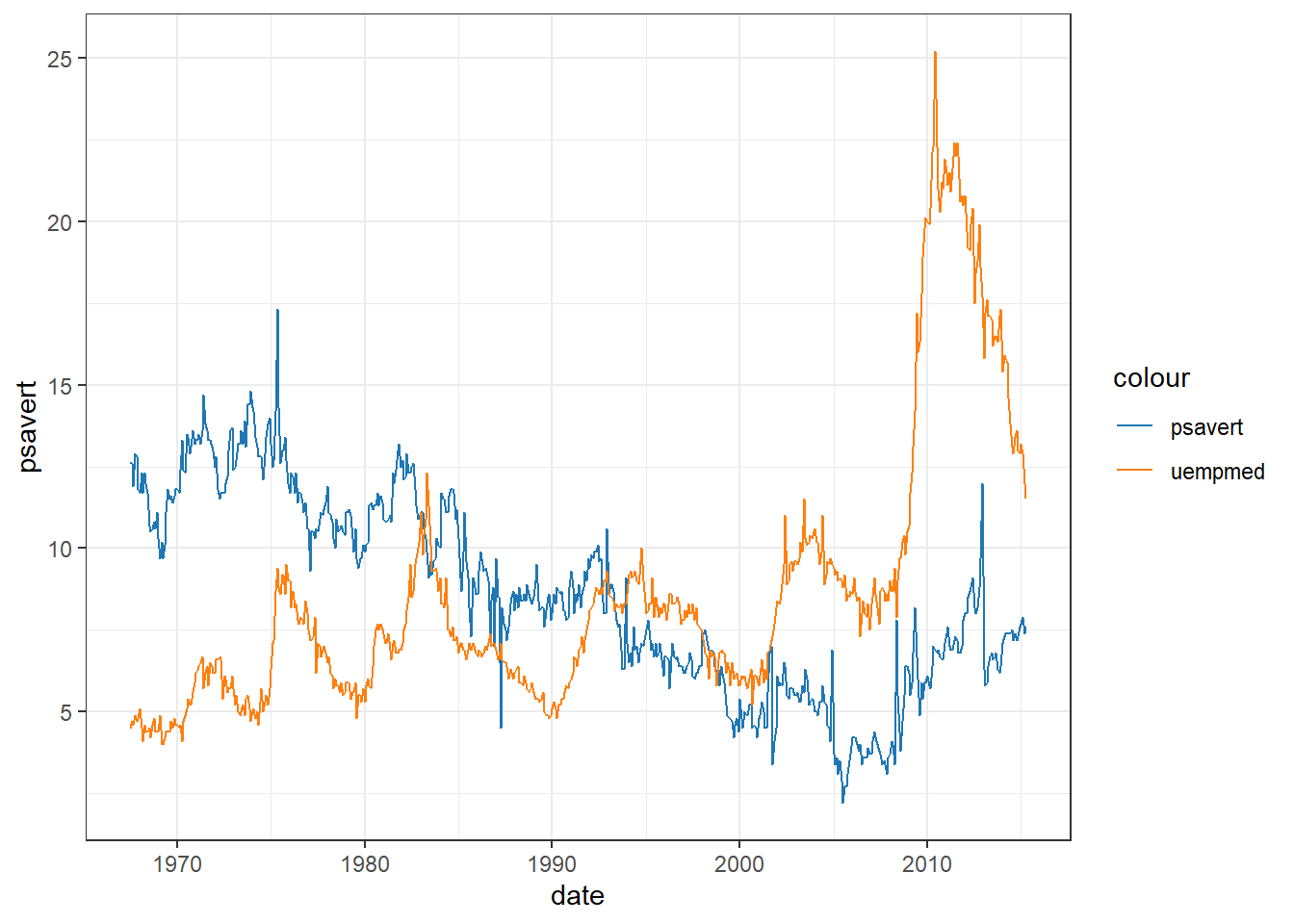
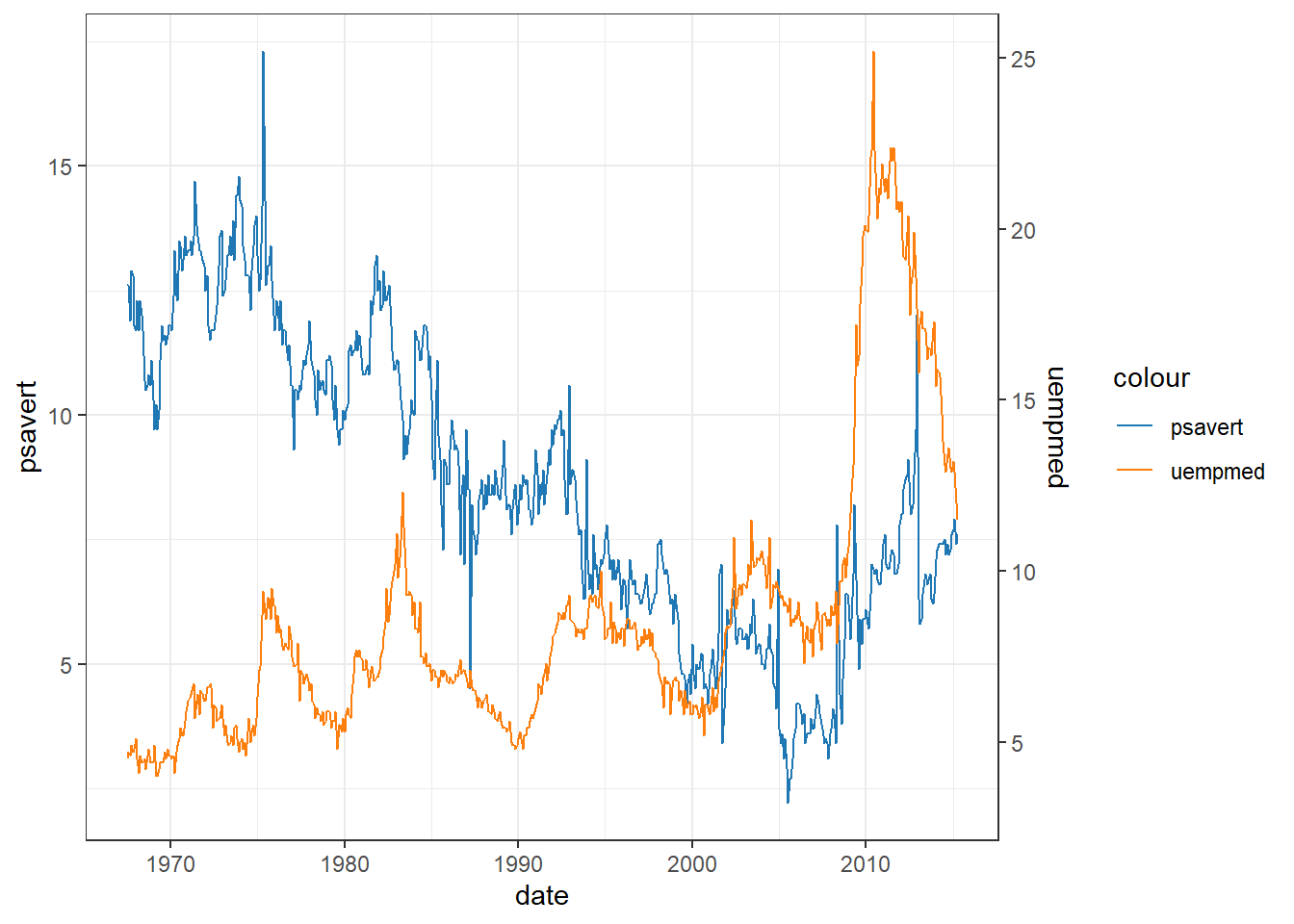
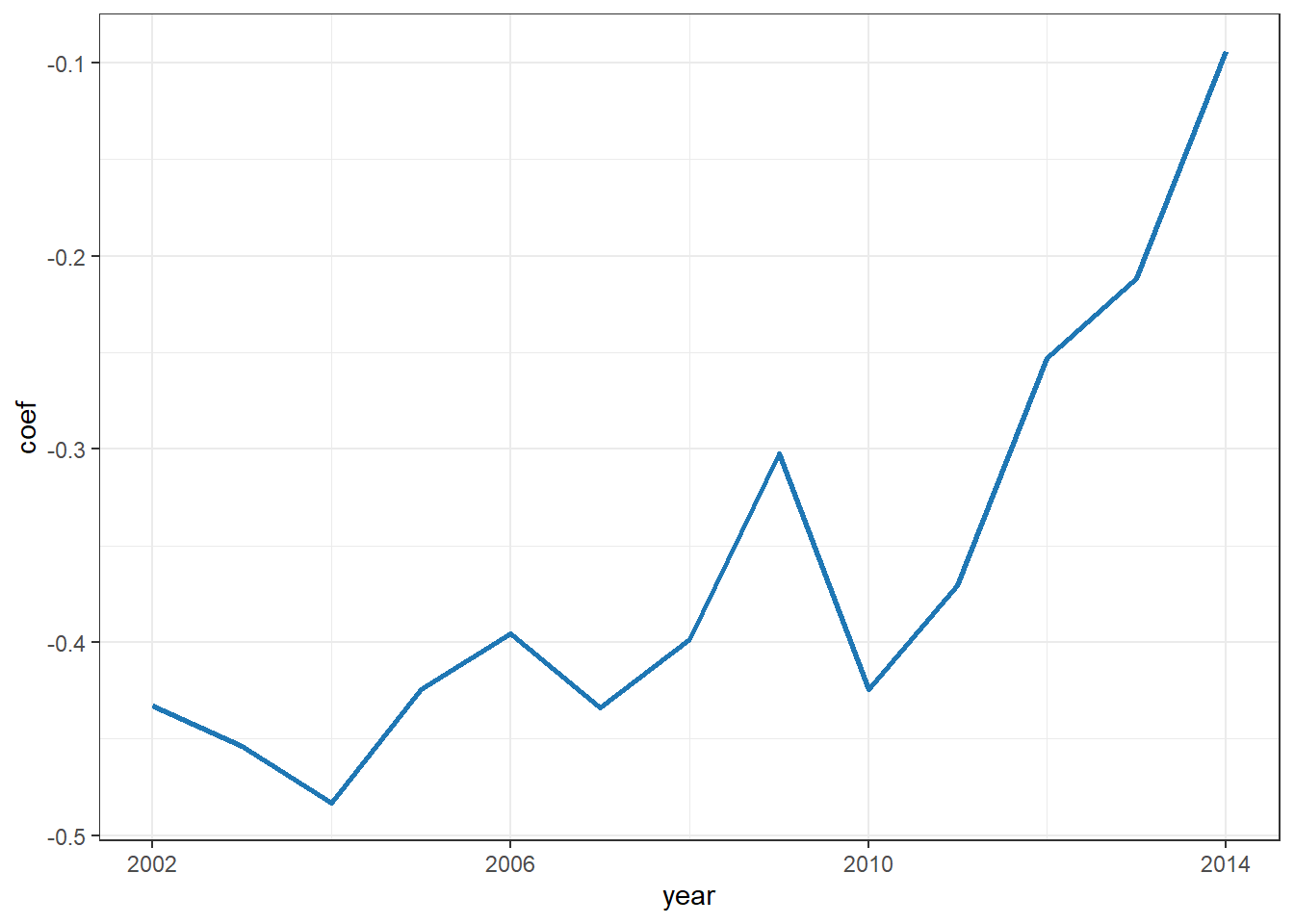
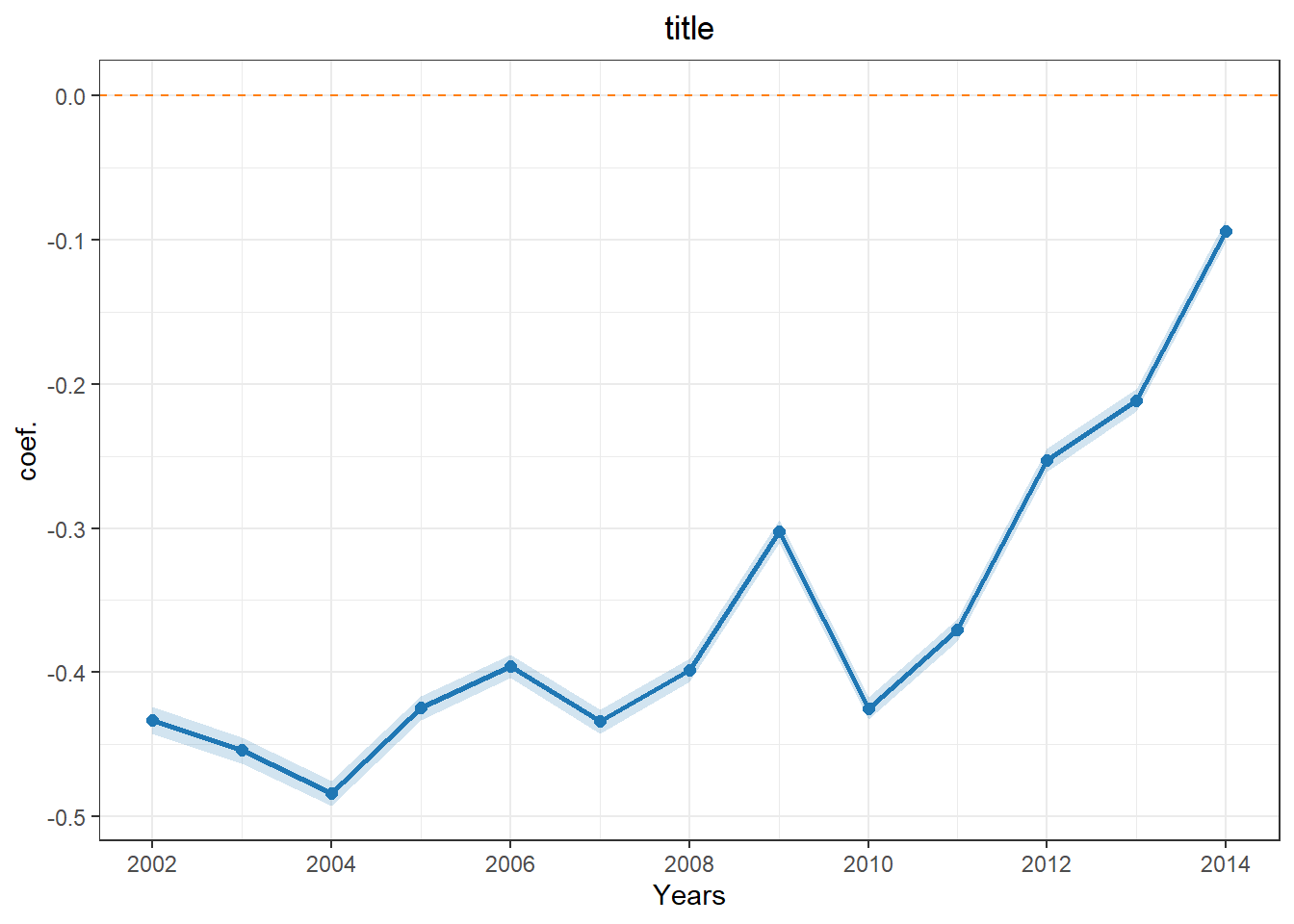
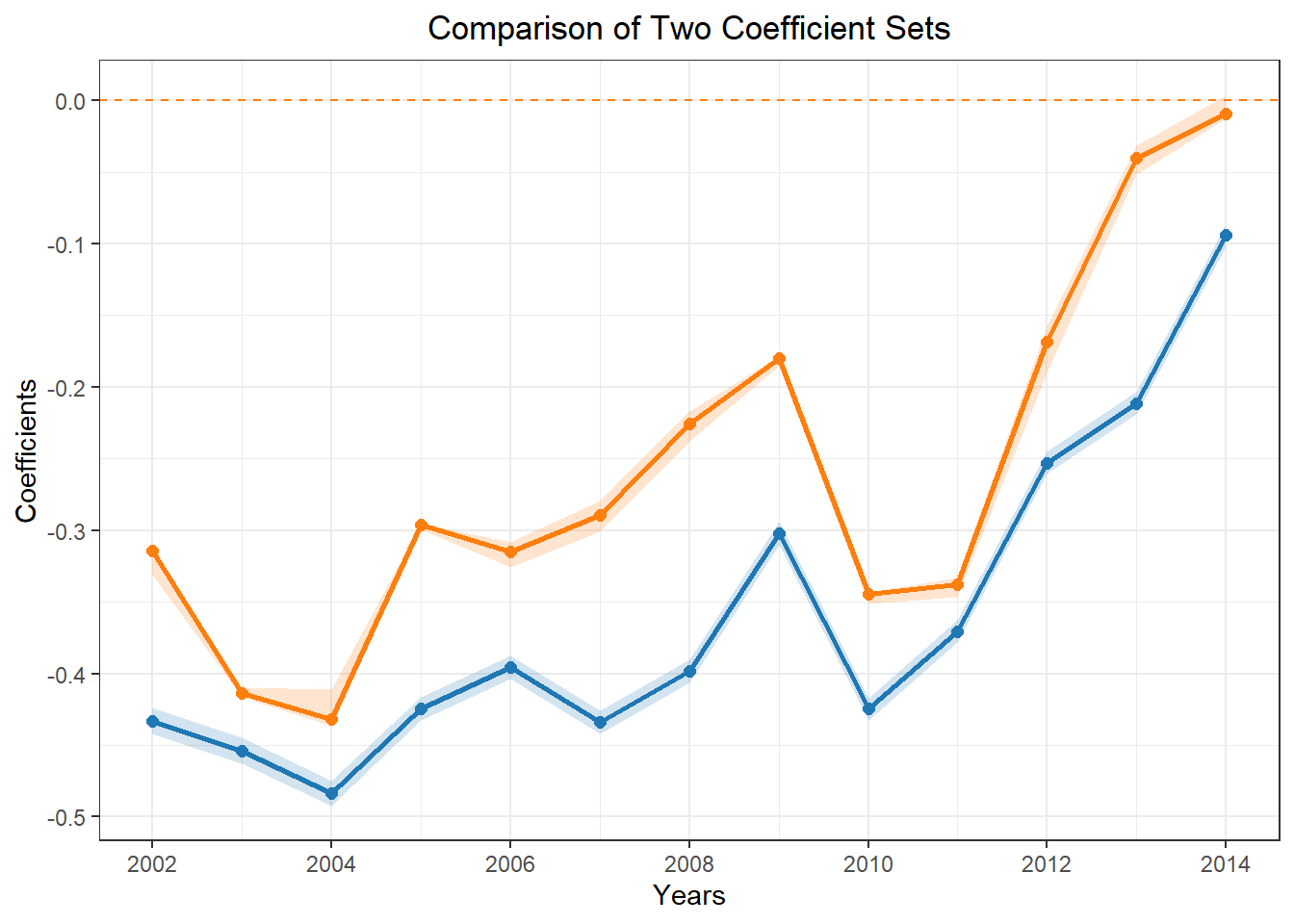
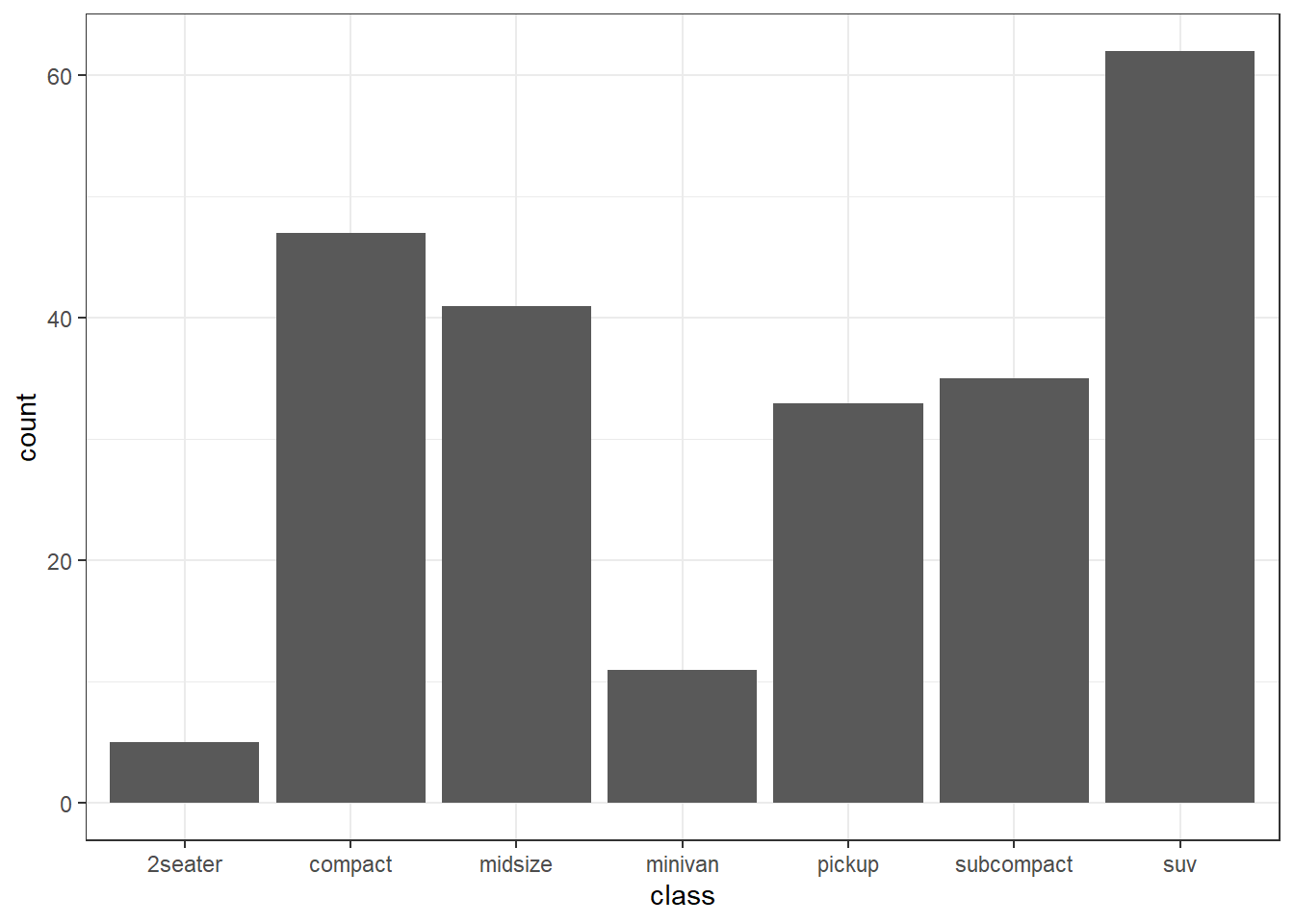
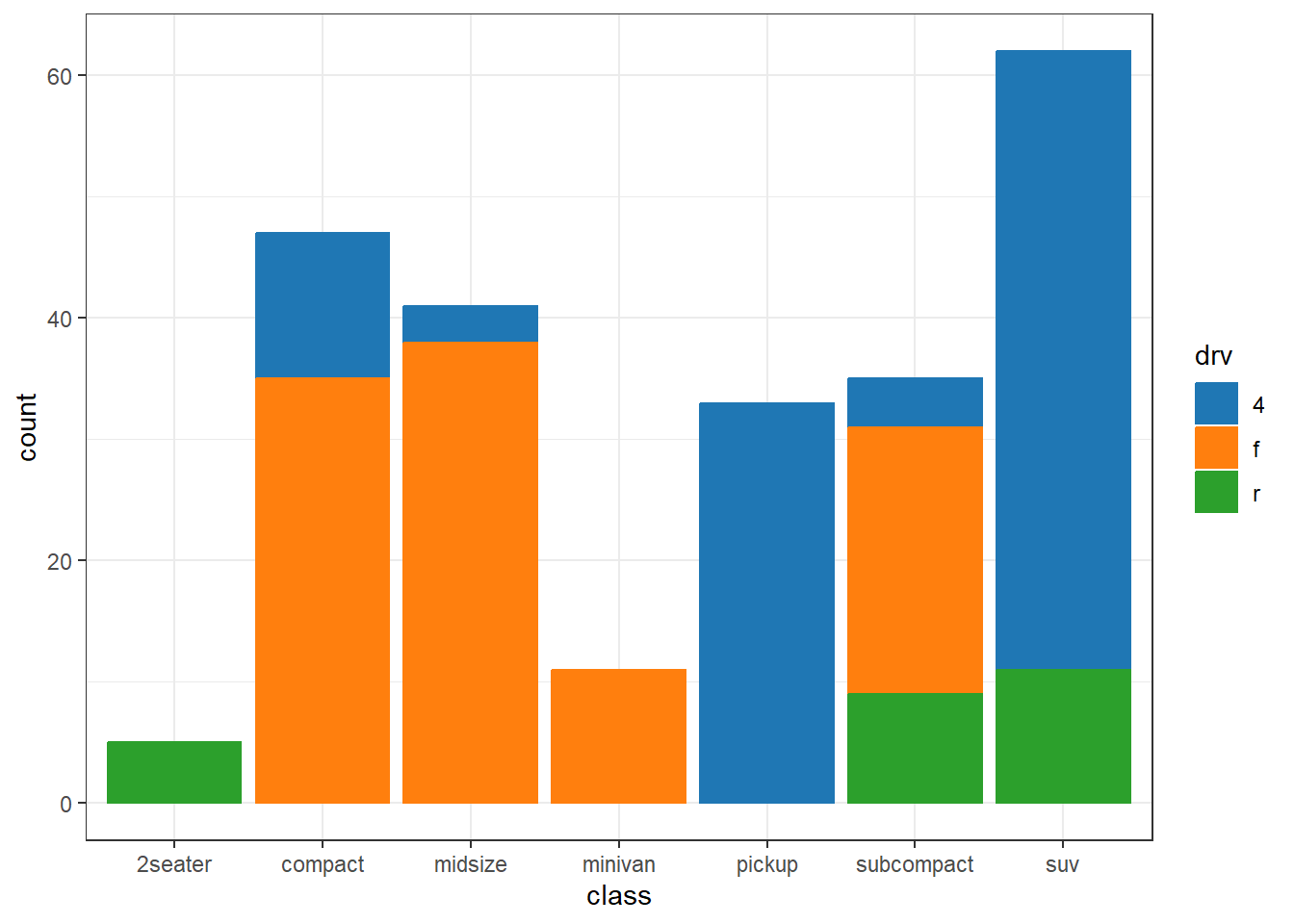
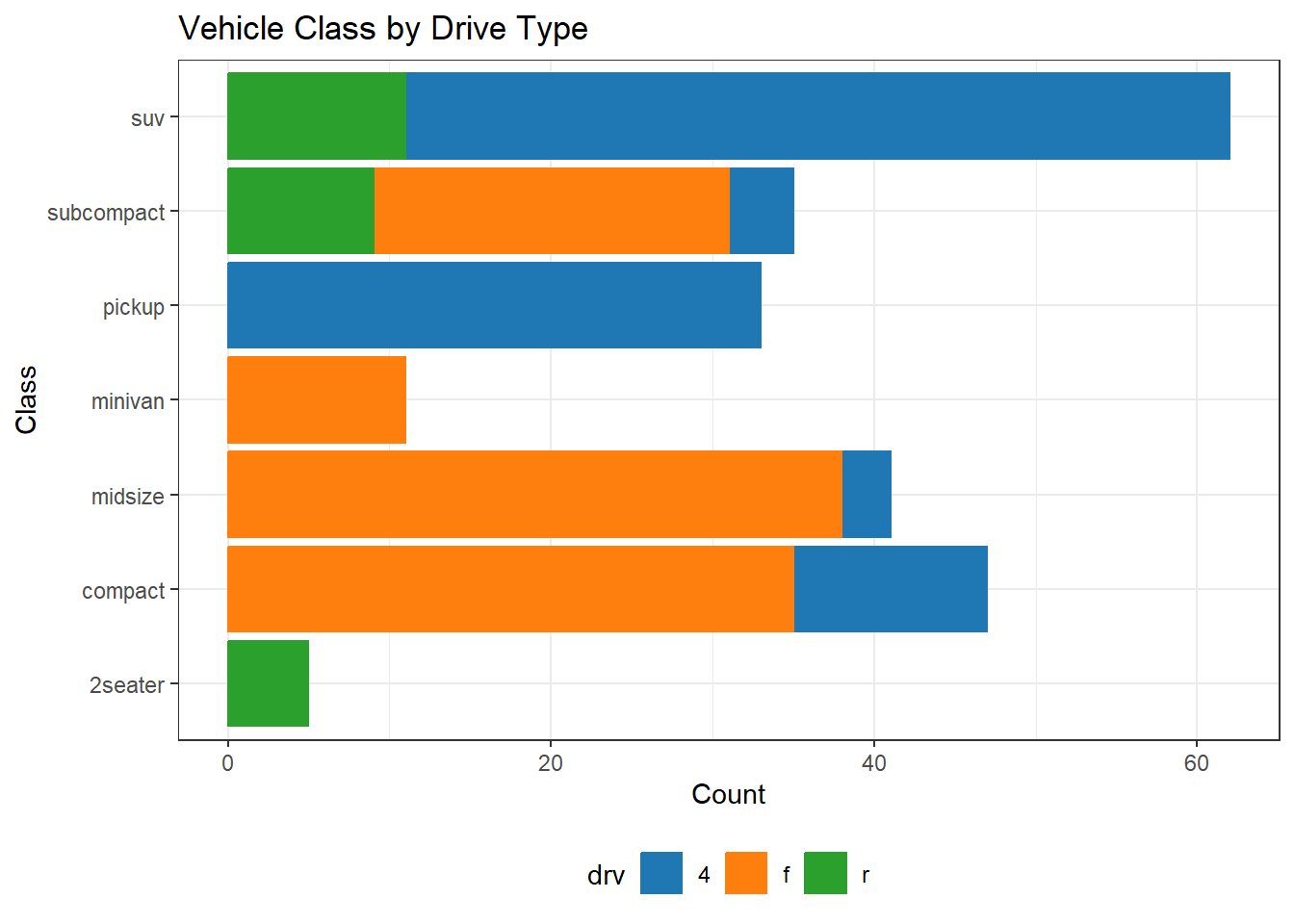
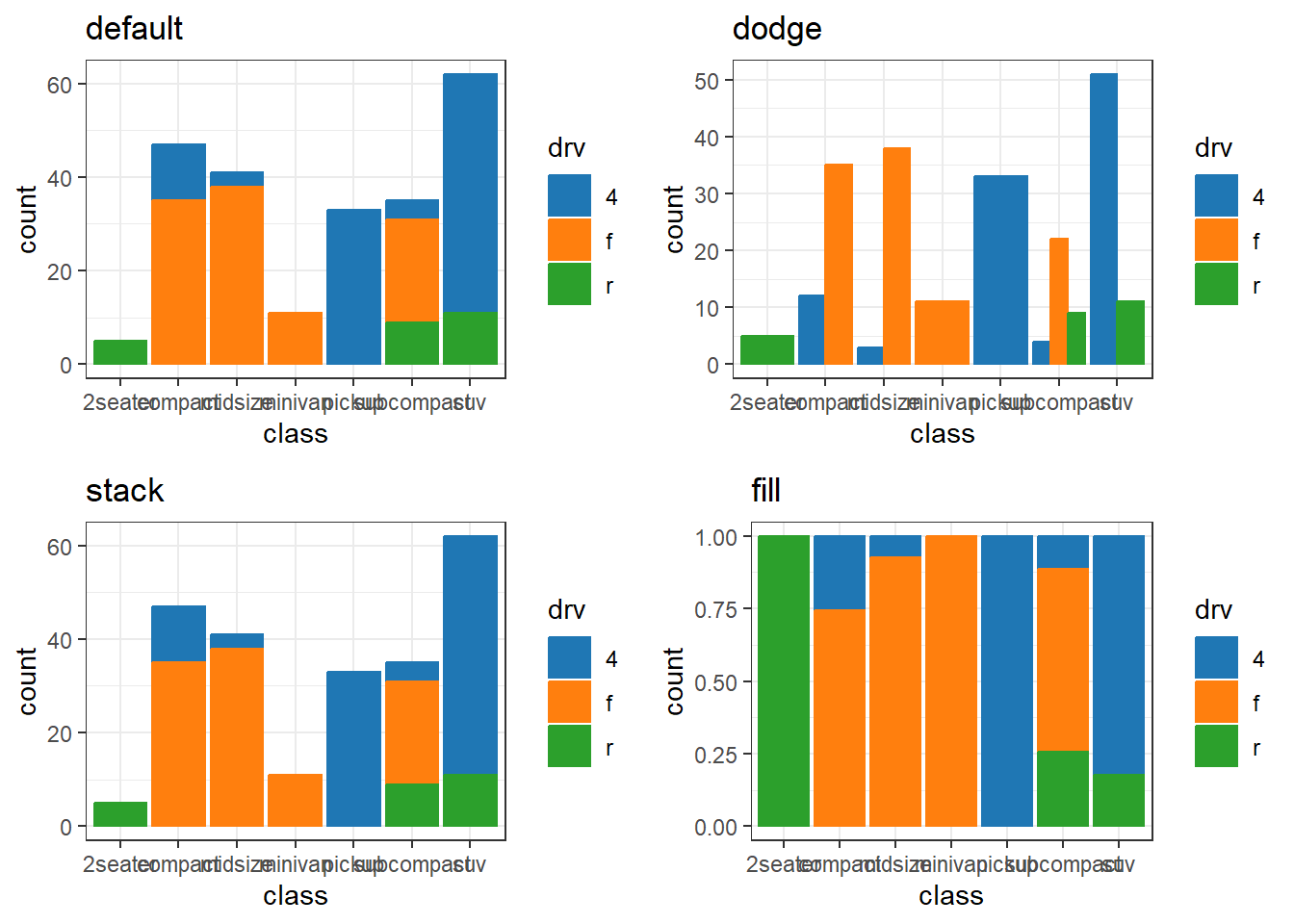
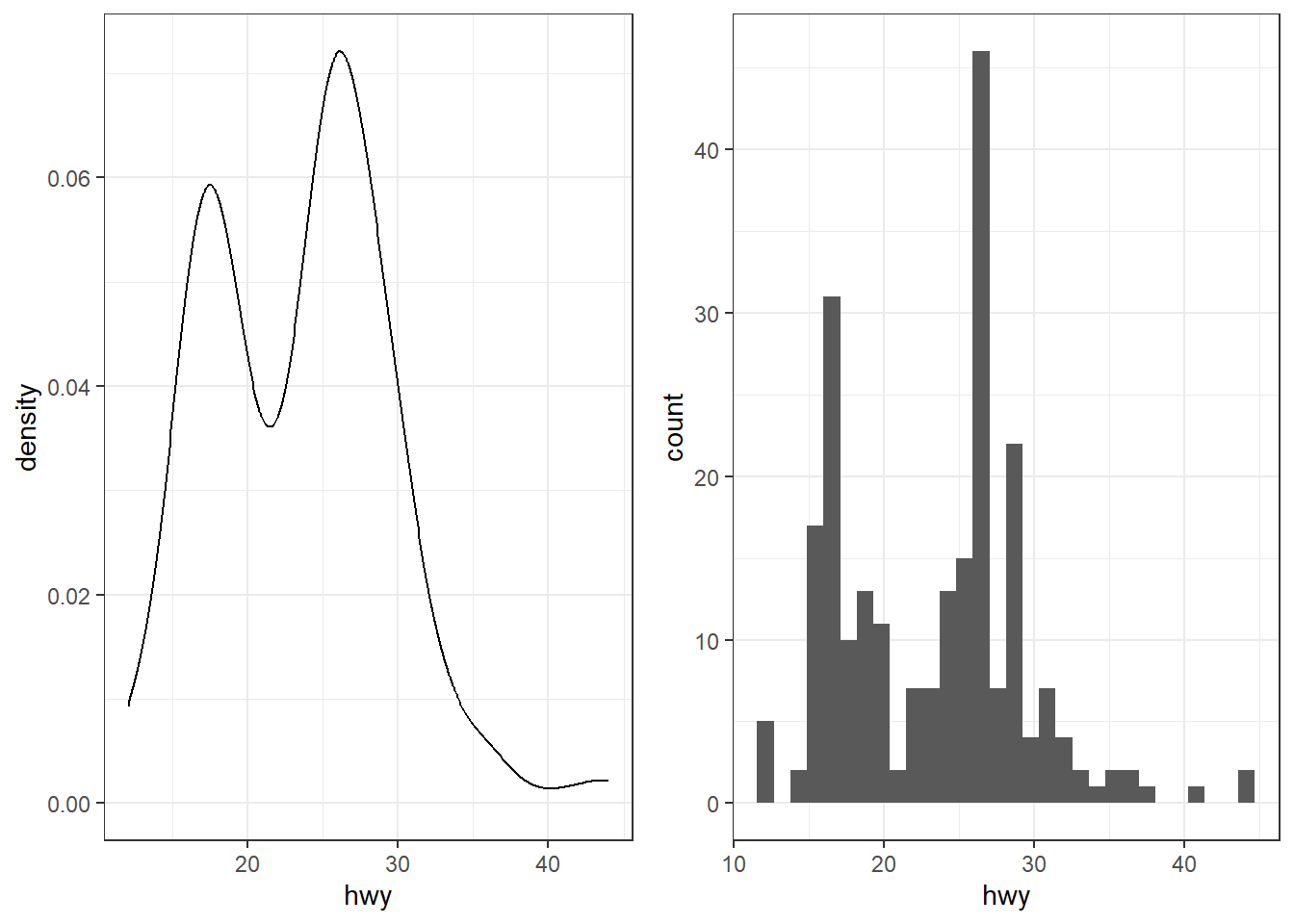
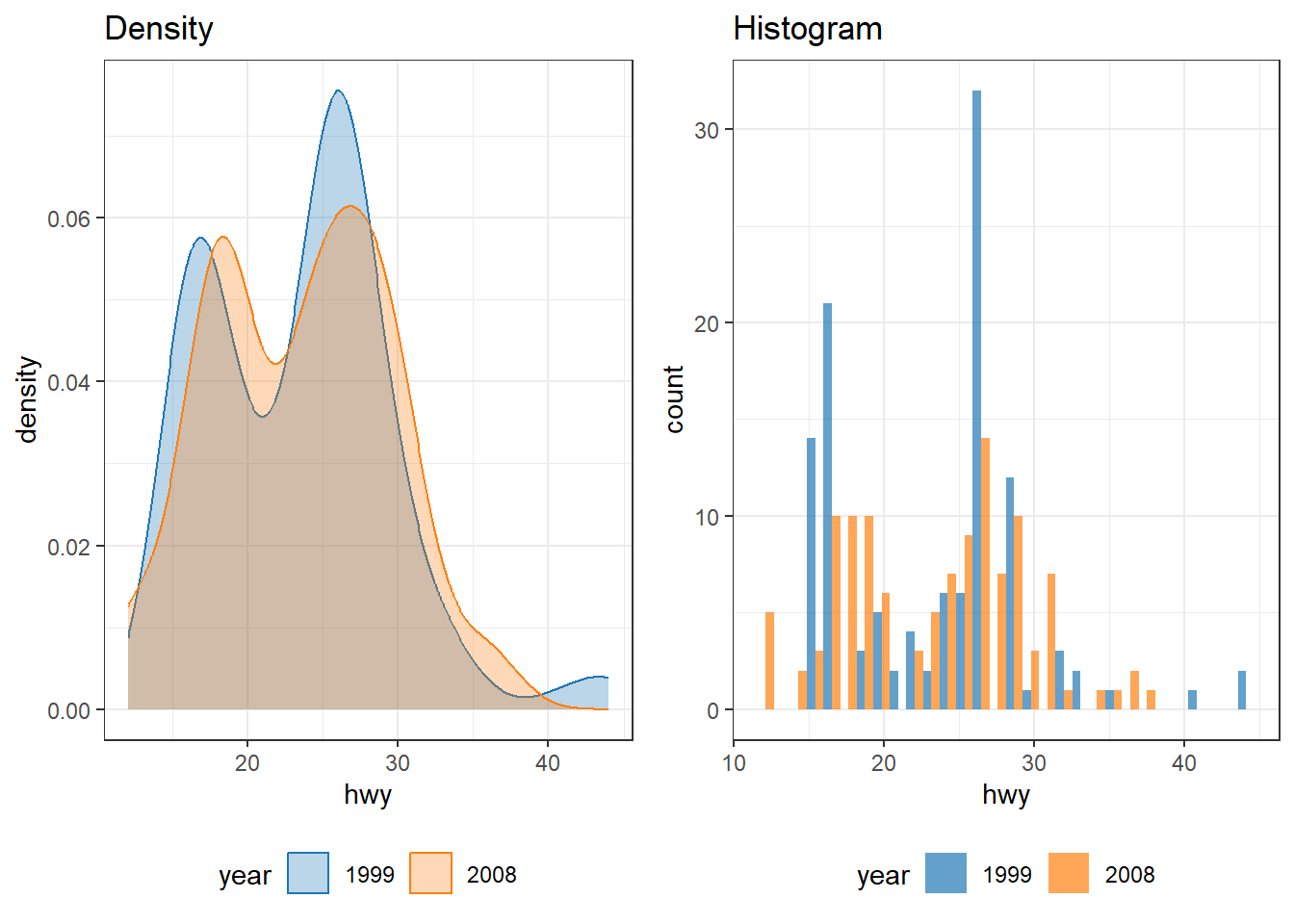
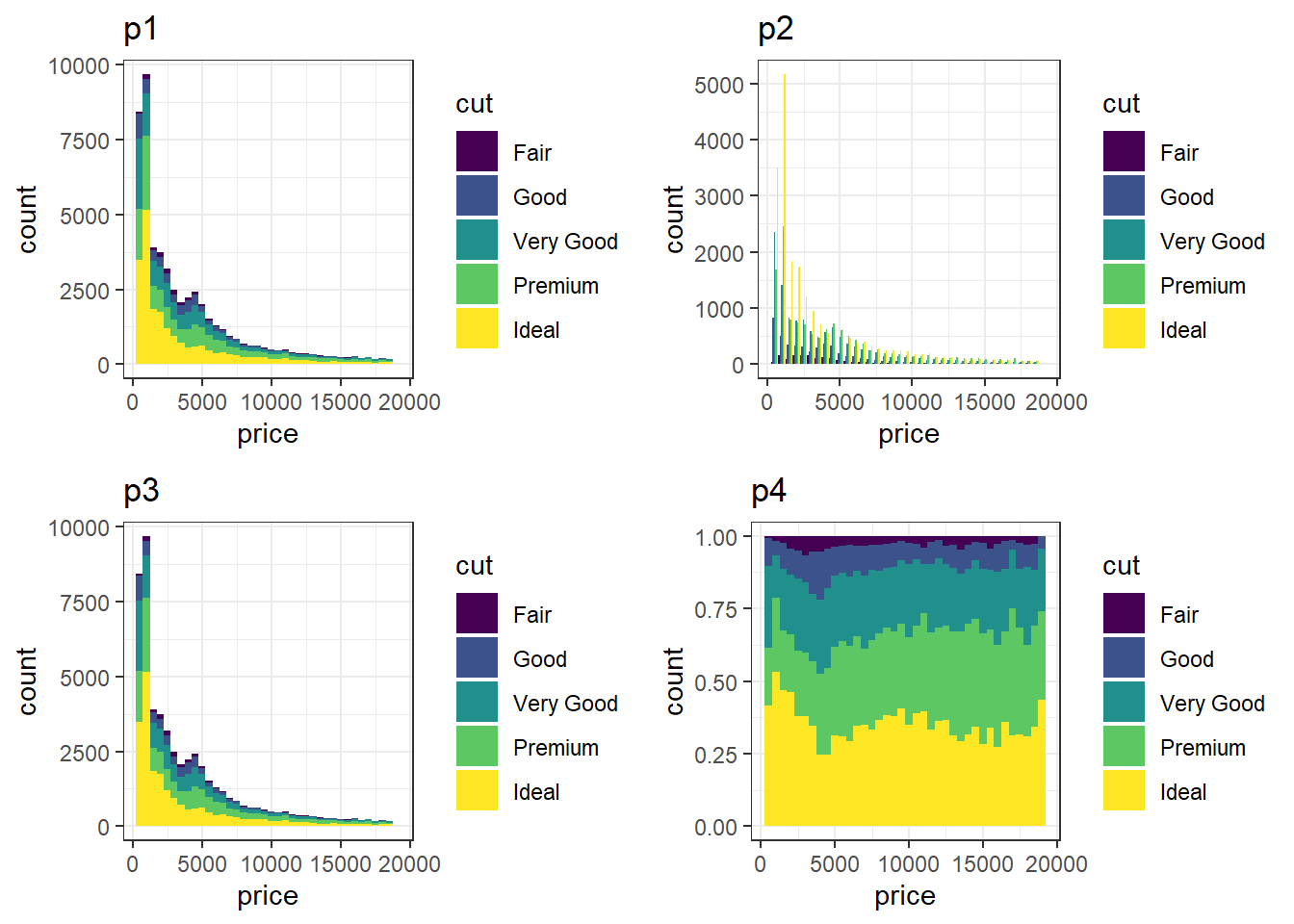
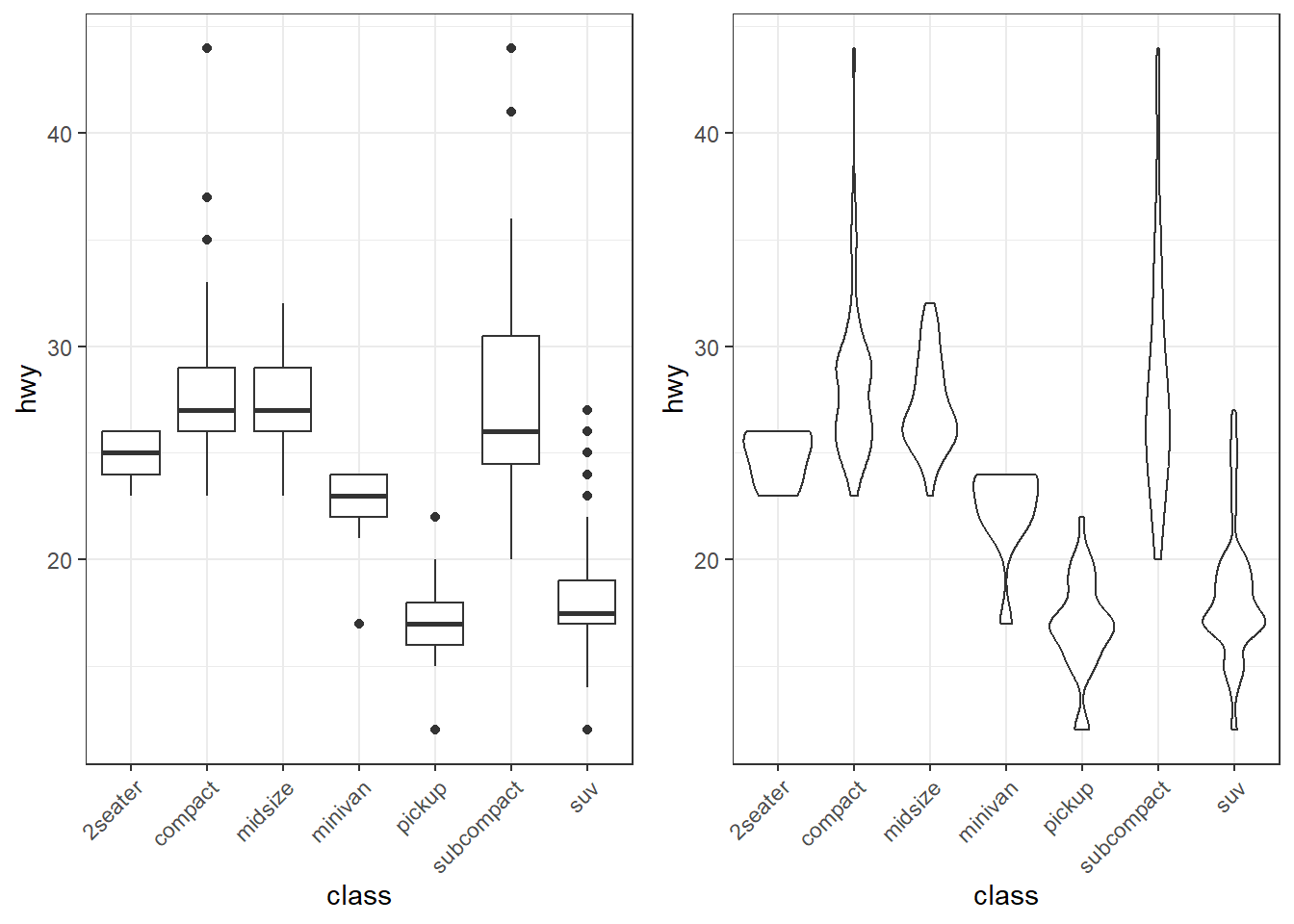
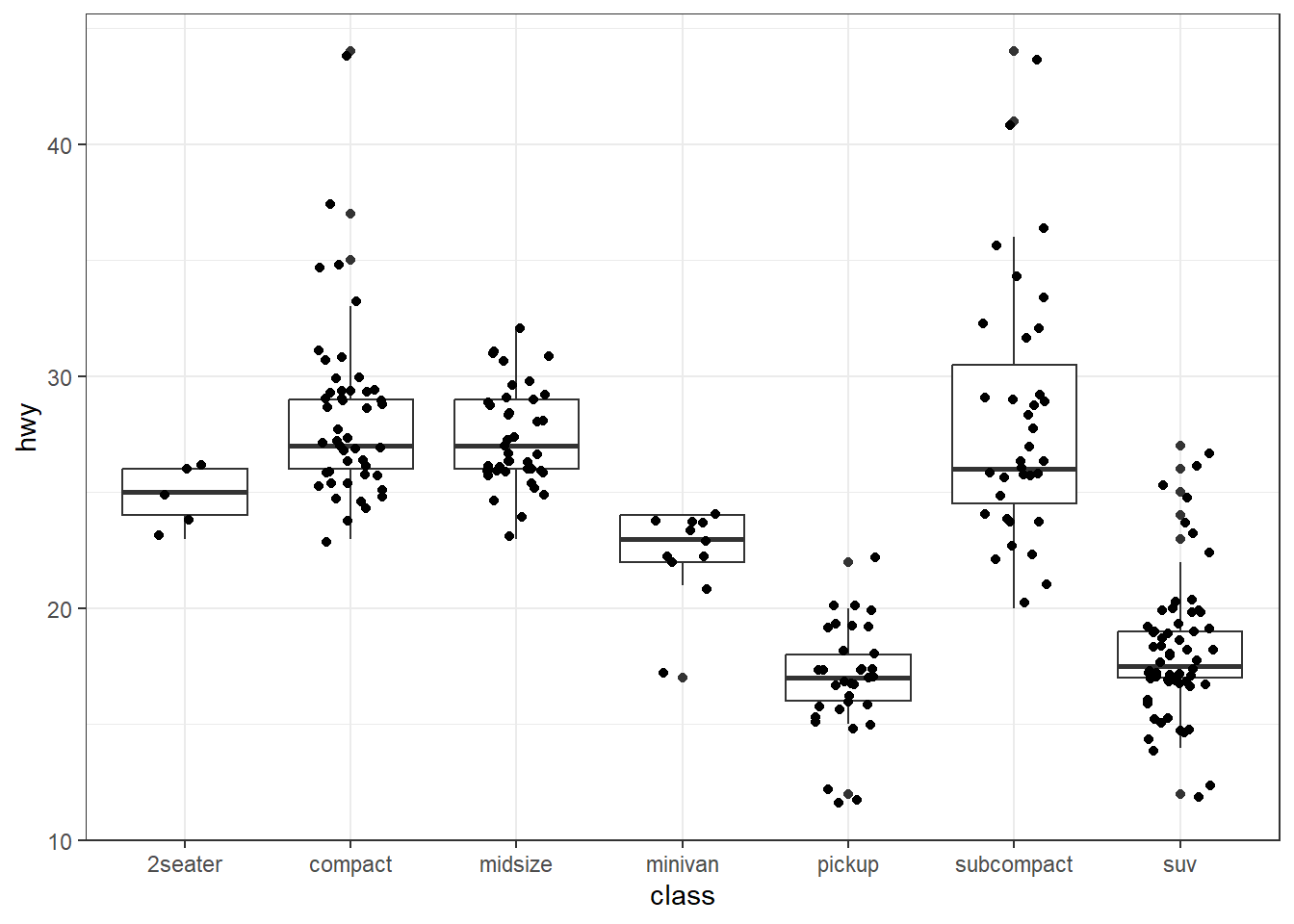
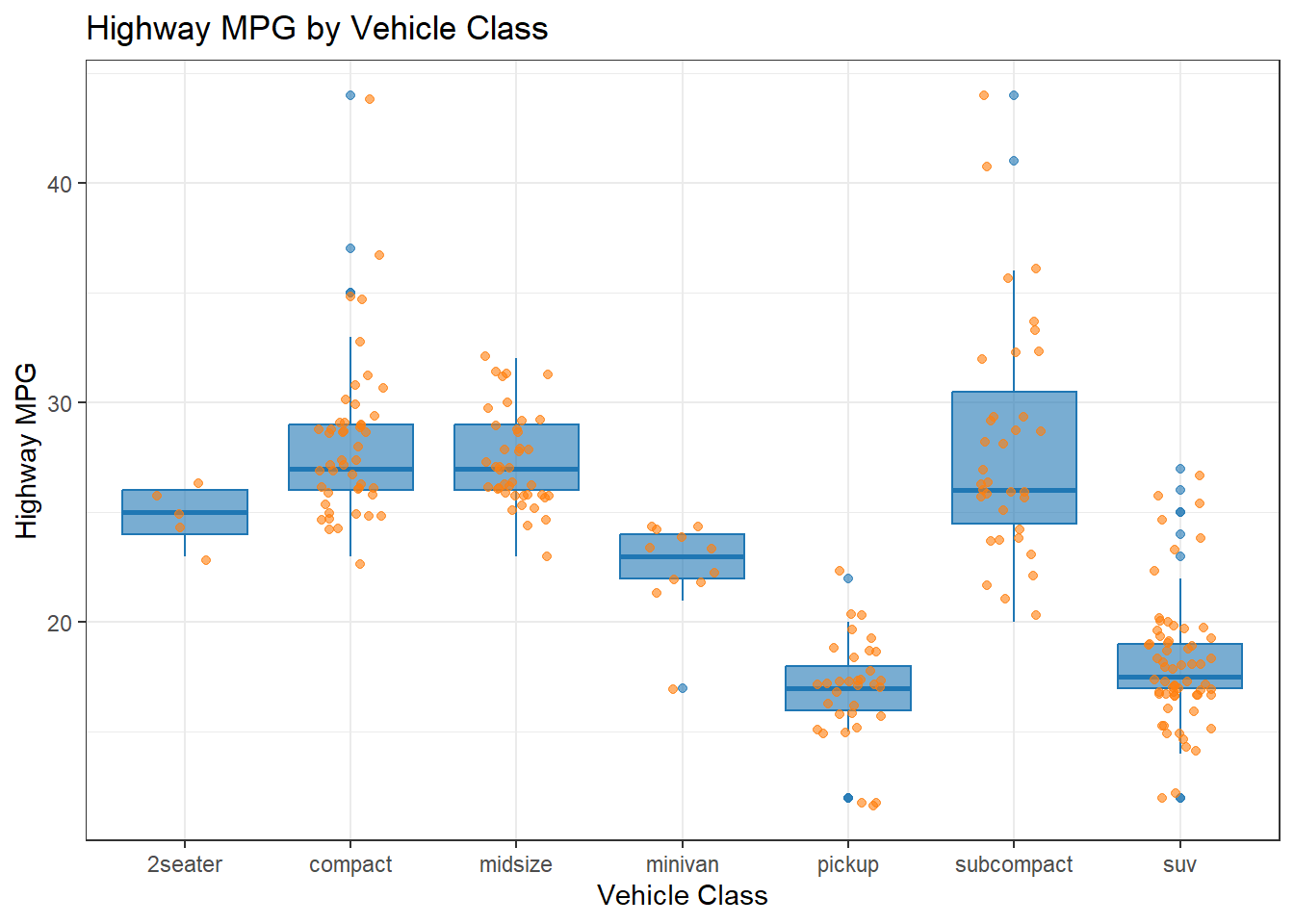
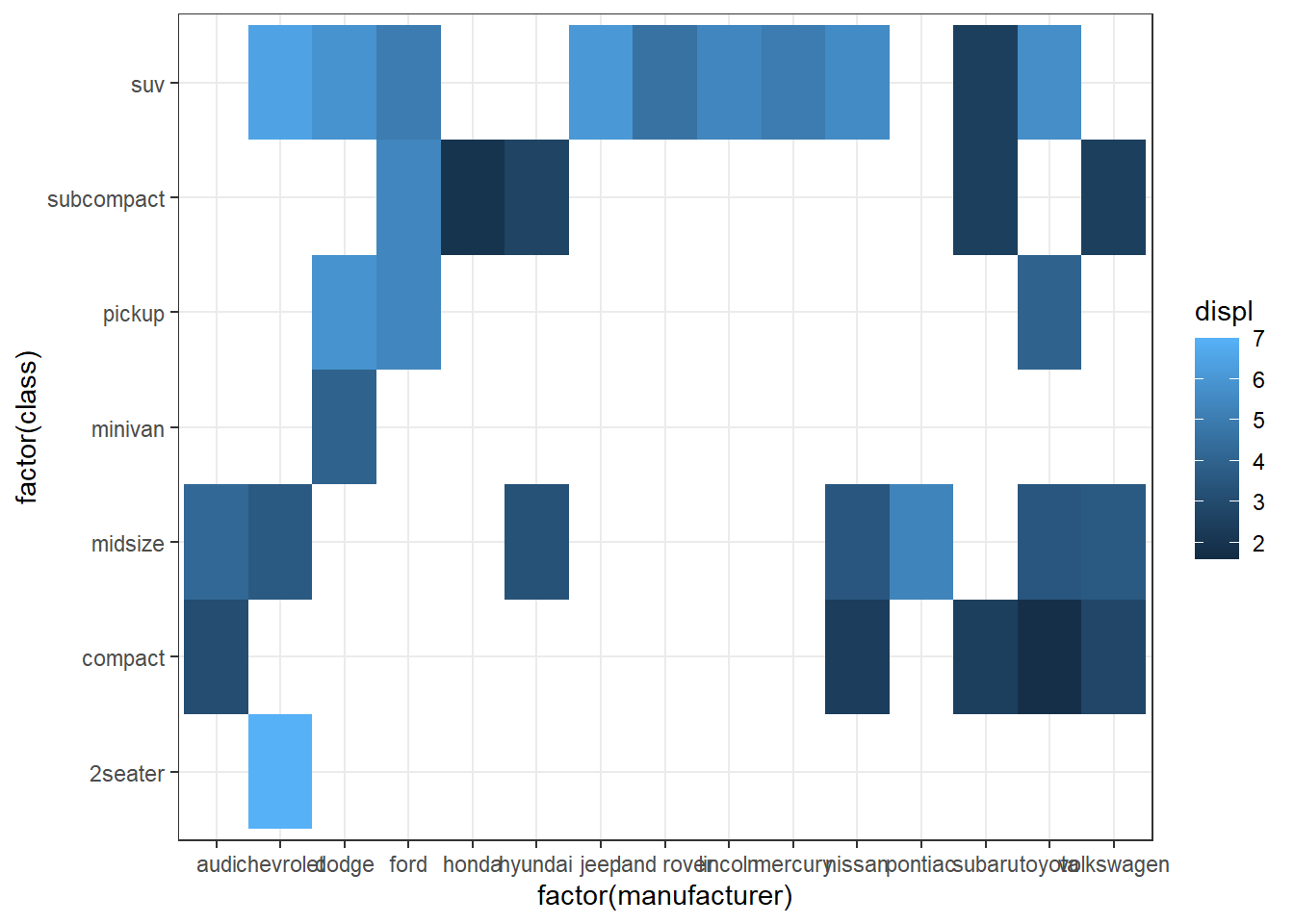
my_colors <- c(
rgb(31, 119, 180, maxColorValue = 255),
rgb(255, 127, 14, maxColorValue = 255),
rgb(44, 160, 44, maxColorValue = 255),
rgb(214, 39, 40, maxColorValue = 255),
rgb(148, 103, 189, maxColorValue = 255),
rgb(140, 86, 75, maxColorValue = 255),
rgb(227, 119, 194, maxColorValue = 255),
rgb(127, 127, 127, maxColorValue = 255),
rgb(188, 189, 34, maxColorValue = 255),
rgb(23, 190, 207, maxColorValue = 255),
rgb(174, 199, 232, maxColorValue = 255),
rgb(255, 187, 120, maxColorValue = 255),
rgb(152, 223, 138, maxColorValue = 255),
rgb(255, 152, 150, maxColorValue = 255),
rgb(197, 176, 213, maxColorValue = 255)
)